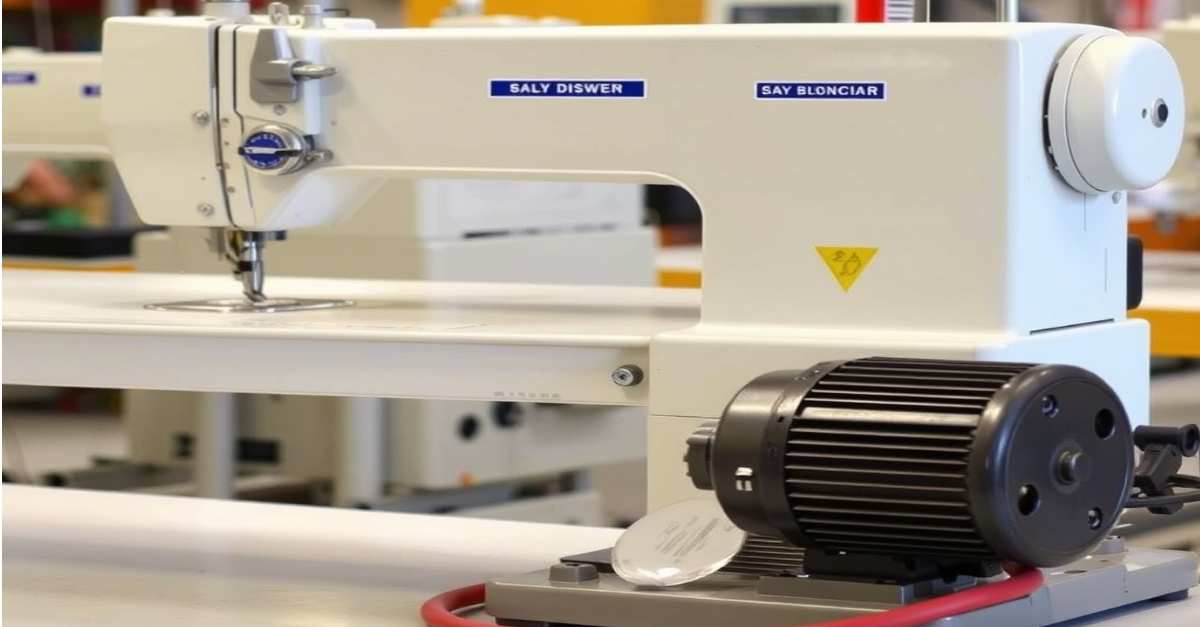
When it comes to industrial sewing machines, choosing the suitable motor is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. While induction motors are commonly used in various industrial applications, they are not the preferred choice for industrial sewing machines. Instead, servo motors and clutch motors dominate this space. Let’s explore why induction motors are not ideal for industrial sewing machines by examining the key aspects of motor performance, cost considerations, and specific requirements of the sewing industry.
Types of Motors Used in Industrial Sewing Machines
Servo Motors

- Precise Control: Servo motors offer precise control over speed and torque, essential for accurate stitching and handling of various materials.
- Energy Efficiency: These motors are highly efficient, reducing operational costs and reducing environmental impact.
- Low Maintenance: Servo motors require minimal maintenance, increasing machine uptime and productivity.
- Upfront Cost: While they are more expensive initially, the long-term savings in energy and maintenance often justify the investment.
Clutch Motors
- High Torque: Clutch motors provide high torque, making them suitable for heavy-duty materials and ensuring consistent stitching quality even at low speeds.
- Durability: These motors are reliable and durable, with a long lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Moderate Energy Efficiency: Although less efficient than servo motors, clutch motors are still more energy-efficient than induction motors.
- Maintenance: Periodic maintenance, such as clutch adjustments and lubrication, is required, which can affect machine downtime.
Induction Motors

- Limited Control: Induction motors lack the precise speed and torque control needed for the diverse operations of industrial sewing machines.
- Lower Energy Efficiency: They are generally less energy-efficient, leading to higher operational costs.
- Higher Maintenance: Induction motors typically have higher maintenance requirements due to the complexity of their components.
- Lower Initial Cost: While they have a lower upfront cost, the long-term operational expenses can outweigh the initial savings.
Performance Requirements for Industrial Sewing Machines
Precise Control and Versatility
Industrial sewing machines must handle various materials and sewing operations, requiring precise control over speed and stitching. Servo motors excel in providing this level of control, whereas induction motors need to catch up.
High Torque for Heavy-Duty Materials
High torque is required for consistent stitching quality on heavy-duty materials. Clutch motors are well-suited for this purpose, but induction motors do not consistently meet these performance standards.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is crucial to reducing operational costs and minimizing environmental impact. Servo and clutch motors are more energy-efficient than induction motors, making them better suited for intensive use in industrial settings.
Low Maintenance
Minimizing downtime for maintenance is essential for maintaining productivity. Servo motors, with their low maintenance needs, are advantageous. Induction motors, however, require more frequent maintenance and checks.
Cost Considerations
Initial Purchase and Integration
While induction motors are cheaper upfront, integrating servo or clutch motors into sewing machines is often worth the higher initial investment due to their superior performance.
Operational Costs

Energy consumption, maintenance, and the need for frequent repairs can make induction motors more costly in the long run despite their lower purchase price.
Lifespan and Durability
Servo and clutch motors offer excellent durability and a longer lifespan, reducing the need for replacements and associated costs.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Energy Efficiency and Production
A textile manufacturing plant that switched from induction to servo motors saw a 15% reduction in energy consumption and a 20% increase in production efficiency. The precise control offered by servo motors played a significant role in these improvements.
Improved Stitching Quality
A garment factory using clutch motors improved stitching quality on thick and multi-layered fabrics, resulting in less material wastage and rework, which positively impacted the company’s bottom line.
Maintenance and Downtime
Smaller tailoring businesses that opted for servo or clutch motors experienced less downtime and lower maintenance costs than those using induction motors, highlighting the financial and operational benefits of the former.
Conclusion
In summary, while induction motors have their place in various industrial applications, they are not the ideal choice for industrial sewing machines. The precise control, high torque, energy efficiency, and low maintenance requirements of servo and clutch motors make them far superior for sewing operations. By investing in the right motor type, businesses can ensure optimal performance, lower operational costs, and greater efficiency.
Call to Action
If you want to upgrade your industrial sewing machines or need expert advice on the best motor options for your specific needs, contact us today for a consultation. Our Team is here to help you make the right choice for your business.











